Home Science Plain Mirror
NCERT Plain Mirror Science Chapter Class 10
Image formation by plain mirror
- The image formed is virtual, erect.
- The size of object is equal to the size of image.
- The object distance is equal to image distance.
- The image is laterally inverted
Note: When a ray is incident normally in a plain mirror the angle of deviation is 180.


Spherical
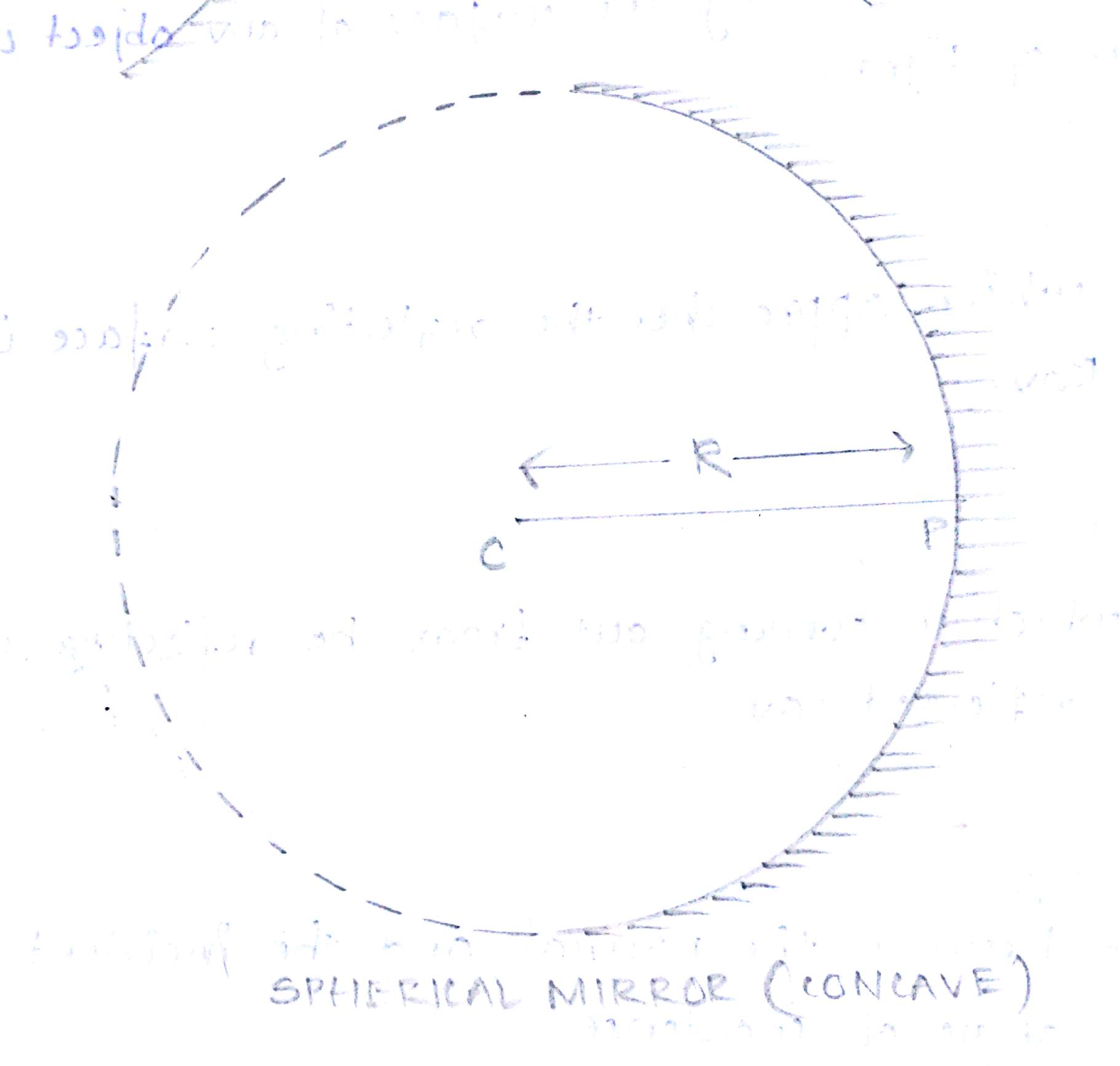
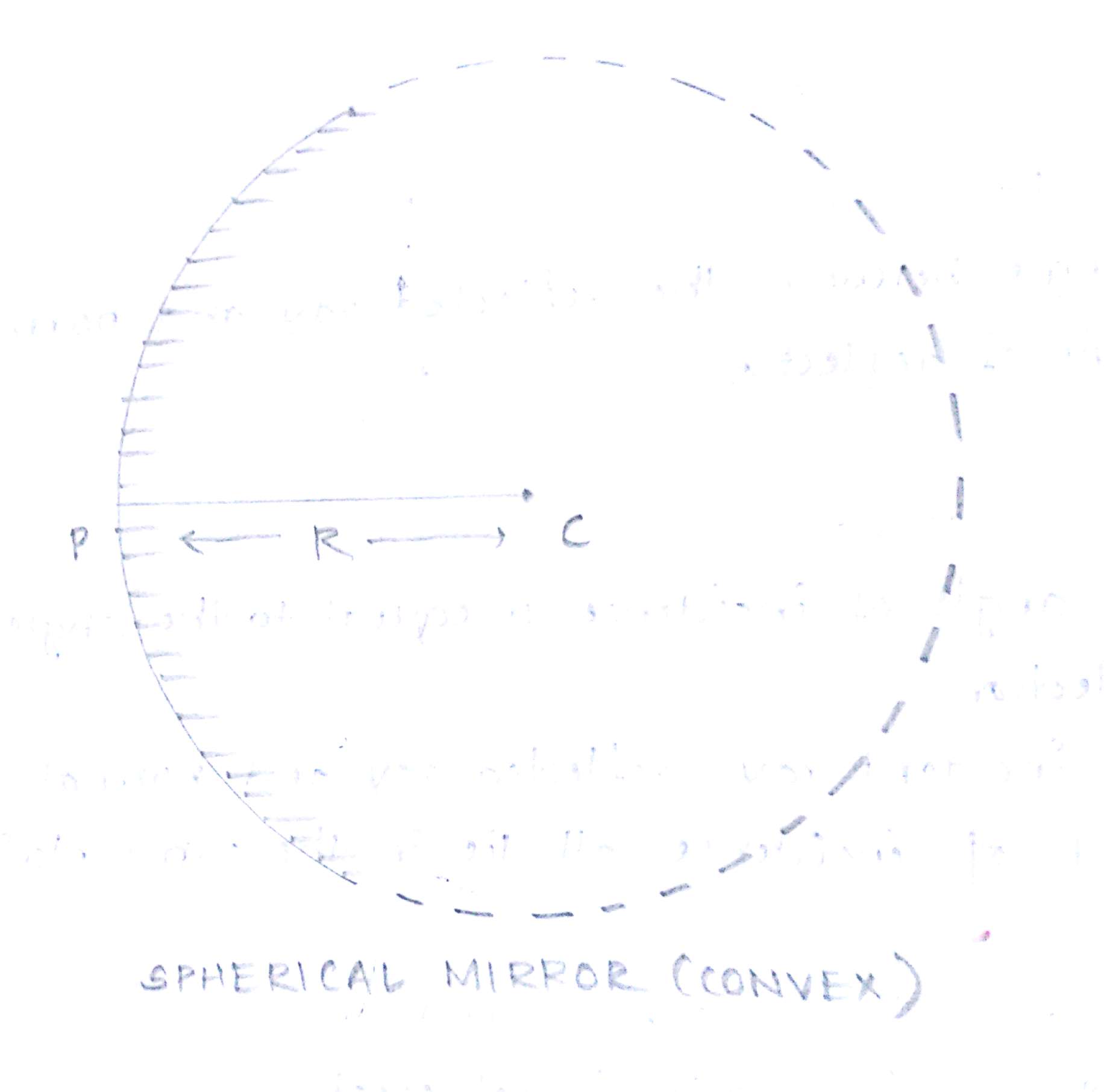
The mirror whose surfaces are spherical is called spherical mirror.
Concave mirror
The mirror whose reflecting surface in curved inward and faces towards the centre is called concave mirror.
Convex mirror
The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outward is called convex mirror.
Terms Related To Spherical Mirror
- Centre of curvature-the centre of the hollow sphere of which the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror forms apart is called centre of curvature.
- Radius of curvature-radius of the hollow sphere of which the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror forms apart is called radius of curvature.
- Pole-the centre of the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is a point called pole.
- Principal axis-the line joining the pole and the centre of curvature of the spherical mirror is called principal axis this line can be extended in both the sides.
- Principal focus-it is the point on the principal axis where the rays of light parallel to the principal axis actually meet after reflection from the spherical mirror.
